The advent of cutting-edge technologies has led to a profound transformation in the healthcare sector, prompting a shift from traditional into a more digitized, connected, and intelligent system. This essay highlights various technological innovations that are pivotal in restructuring healthcare. We delve into the digitization of health records and the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into the industry, exploring the value they offer and the potential hurdles they present.
We further explore telemedicine’s rise, the impact of wearable technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare, and how blockchain technology is used to improve data security and interoperability. Each segment presents a balanced perspective on the progress, challenges, and potential solutions for the respective topic.
The Digitization of Health Records
Transforming the Landscape of Healthcare
The dawn of the digital age spurred a reinvention across myriad verticals, none more so than within the healthcare sector. An area where this metamorphosis has been compellingly clear is the digitization of health records—a shift that has altered the landscape of healthcare in numerous significant approaches.

Traditionally, health records were paper-based, necessitating acres of storage area and immense manpower to catalog, retrieve, and interpret the data. Not only was this model unsustainable from a cost perspective, but it also introduced scope for human error and complicated the process of data analysis. Moreover, access to these records was, often, geographically limited and time-consuming.
Enter digital health records. Digitization brought down these barriers and ushered in an era of accuracy and convenience. Leveraging the potential of technological advancements, health information is now meticulously recorded, organized, and stored digitally. This eases the process of assimilation of patient history, prior diagnosis, medication, and critical notes from healthcare specialists, effectively creating a precise, comprehensive view of an individual’s health.
One notable alteration in the healthcare landscape brought on by this digitization is the unprecedented ease of accessibility. Healthcare professionals can now retrieve information at the click of a button, regardless of their physical location. This instant access can significantly accelerate decision-making processes, enabling prompt medical intervention and reducing the potential for medical errors.
Moreover, digitized health records pave the way for a more collaborative healthcare approach. The patient, the physician, the nursing staff, and specialists all can view and append records, fostering an environment of shared information and insights, thereby enhancing the quality of care provided.
Additionally, the transition to digital records has facilitated efficient population health management. Data once trapped in file cabinets are now readily available for insightful analyses. Through data aggregation and advanced analytics, healthcare providers can identify trends, evaluate risk factors, and implement preventive measures on a community scale—a capability that was barely conceivable in the era of paper-based records.
Nevertheless, digitization is not devoid of challenges. Data privacy and security concerns, interoperability issues, and the hurdle of implementing wide-scale digital literacy among health practitioners are matters demanding attention. Also, developing nations still grapple with the enormity of moving their vast pile of paper records into the digital universe.
Collectively, the digitization of health records has heralded a transformation in healthcare—one that prioritizes speed, accuracy, and collaboration. It propels healthcare towards a future characterized by data-driven insights and empathetic care, bridging gaps between the people who need care and those who provide it.
Yet, the change is an ongoing process. Meeting challenges head-on, mitigating associated risks, and continually iterating technological advancements will be essential to fully realize the power of this digital revolution. As with any transformational journey, perseverance and adaptability will dictate the course of progress in unfolding chapters of digital health records.

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Healthcare
As our collective understanding of artificial intelligence (AI) deepens, its influence seeps further into diverse sectors of our global society, yet perhaps none as significantly as healthcare. The integration of AI into this critical space augments beyond the digitization of health records and into a realm of not just data utilization, but also predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, and a transformative approach to healthcare management.
Forecasting health trends and predicaments is an observational task long-flawed from dependency on human discretion. Still, the introduction of AI allows for the creation of predictive models based on pattern recognition and statistical analysis. The ability of AI to discern and foresee potential outbreaks or medical emergencies points toward the possibility of proactive, rather than reactive, healthcare strategies.
Moreover, ground-breaking strides have been made regarding mapping the human genome, and AI is enabling the actualization of personalized medicine in the form of genomics and proteomics. Through machine learning algorithms and computational techniques, AI can interpret patterns within vast amounts of genetic data. This roadmap is the way toward treatment programs tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, revolutionizing therapeutics by replacing a one-size-fits-all model with precision medicine.
Furthermore, AI is set to transform the face of medical diagnosis and treatment plans. With machine learning systems capable of recognizing patterns and images, diseases such as cancer could be detected with near-perfect accuracy at much earlier stages. Robots equipped with AI are also making waves in the field of surgery, able to perform intricate procedures with minute precision, minimizing surgical invasion and subsequent healing time for patients.
Taking a step back to survey the whole healthcare system, AI’s capacity for integrative and efficient management cannot be overlooked. It paves the way for better coordination of services, tracking resource allocation and patient flows, and identifying opportunities for process enhancement. The eventual outcome: optimized health systems with improved patient experience and outcomes.
The complex dance of integrating AI into healthcare is fraught with challenges, including ethical considerations related to AI decision-making and the potential loss of the human touch in an inherently human field. Yet, the palpable excitement within scientific and academic circles underscores a shared belief that these hurdles are indeed surmountable. Comprehensive training, robust legislation, and continuous technological innovation will be key to resolving these dilemmas.
As we press forward in our quest for advancements in AI within healthcare, it must be remembered that our journey is one of responsible exploration. The goal remains improving health outcomes, reducing disparities, and effecting equitable healthcare for all. AI’s potential contributions to these objectives are considerable yet must be pursued with unwavering diligence in managing the plausible risks associated with AI integration into healthcare. This field rests on the precipice of a revolution, one that will alter the very core of healthcare practice, offering transformative possibilities for improved human health. AI stands as a fundamental pillar in this brave new world of healthcare, an agent of change that promises to indelibly shape its future.
The Rise of Telemedicine
Moving from the realm of health digitization and artificial intelligence, we come to the transformative discipline of telemedicine. Recent advancements have witnessed telemedicine gaining momentum in the healthcare landscape, heralding an era of increased accessibility and efficiency.

Telemedicine, the use of digital technologies to deliver medical care remotely, is at the forefront of tackling healthcare access disparity. Where conventional care is bounded by geographical limitations, telemedicine transcends these restrictions, offering a viable solution for patients residing in remote or rural areas, elderly confined to homes, or those with mobility constraints. With a simple internet connection, medical consultation, follow-ups, and health education are no longer privileges only the urban dwellers enjoy.
In the context of public health emergencies – a case in point, is the recent COVID-19 pandemic, the value of telemedicine crystallized further. It proved to be pivotal in flattening the curve by curbing unnecessary hospital visits, thus reducing the risk of transmission and minimizing both patients and healthcare staff’s exposure. Virtual consultations became the new norm, undeniably demonstrating the capacity of telemedicine to enhance healthcare delivery flexibility in times of crisis.
Complementing accessibility, telemedicine is also making strides in the realm of healthcare efficiency. It manifests in shorter wait times and travel elimination, thus allowing patients to direct their time and resources more effectively. Moreover, enabling healthcare providers to evaluate, diagnose, and treat patients remotely, amplifies their ability to manage their load and optimize care.

Furthermore, telemedicine’s potential in chronic disease management is worth expounding. By facilitating regular monitoring and immediate feedback, telemedicine ensures patient adherence, mitigates complications and improves overall healthcare outcomes. This, not only results in more efficient patient management but also reduces the burden on the healthcare system, given the high costs associated with chronic disease treatment.
While telemedicine carries evident potential, it comes with its share of caveats that warrant meticulous consideration. There is a persistent risk of misdiagnosis due to the absence of physical examination, compounded by a potential for lower-quality patient-provider interaction. The digital divide further threatens to create inequality in telemedicine access. Lastly, there exist pertinent concerns about cybersecurity and patient data privacy that require stringent safeguards.
Undoubtedly, telemedicine is reengineering the conventional healthcare landscape. It promises a more accessible and efficient future, although with the necessary attention to ethical considerations and potential drawbacks. As we forge ahead to redefine healthcare boundaries, the role of telemedicine is destined to become increasingly central. In essence, what was once regarded as healthcare’s auxiliary component is now steering its transformation to ensure healthcare for all, anytime and anywhere.
Healthcare Wearables and IoT
Infusion of Healthcare Wearables and IoT Devices in Personalized Medicine
Following the digital march in healthcare, the arenas of healthcare wearables and Internet of Things (IoT) devices have witnessed an evolutionary leap. The intersection of wearable technology and IoT with healthcare provisions offers nuanced alerts to possible health issues, promotes proactive health management, and contributes to the individualization of medical treatment, appropriately referred to as personalized medicine.
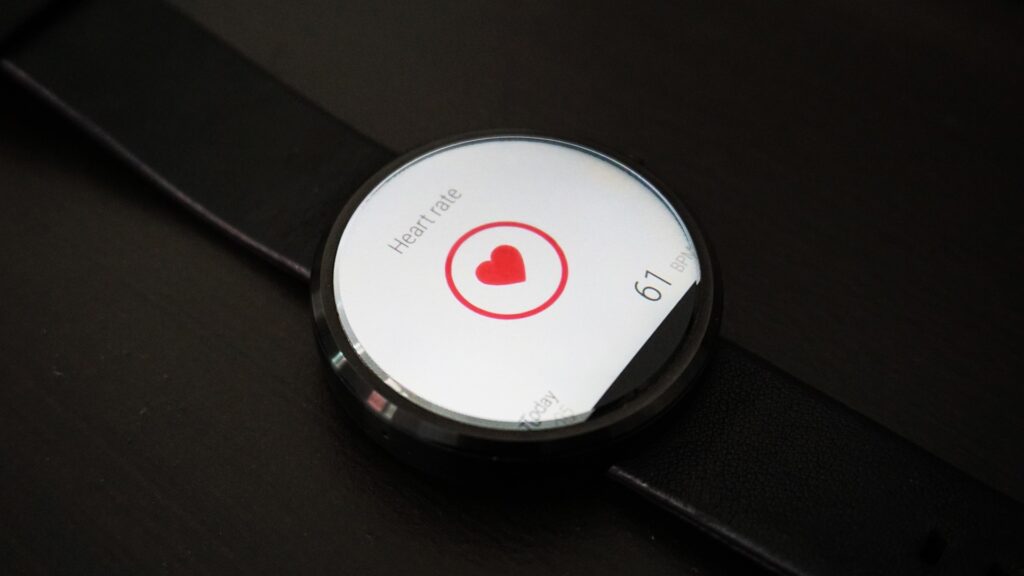

Healthcare wearables, which include smartwatches, wearable fitness trackers, and clothing with embedded biometric sensors, have radically disrupted the manner of health monitoring. Enabled by IoT, such devices have moved beyond mainstream uses, offering the ability to monitor numerous physiological parameters including respiratory rates, oxygen levels, body temperature, electrocardiogram (EKG) readings, and sleep patterns. The continuous streaming of such individual-level health data is instrumental in revealing trends, indicating potential health concerns, and enabling prompt medical intervention.
The applications of IoT extend to implantable medical devices, which range from pacemakers to insulin pumps. These devices now serve two roles simultaneously – delivering therapeutic effects and monitoring in-vivo physiological responses which can be wirelessly communicated to healthcare teams for meticulous monitoring and modulations in medical strategies, if required. This integration forms the basis for personalized therapy, tailoring medical interventions to an individual’s needs and responses.
Moreover, the convergence of wearable and IoT technologies with smartphone applications has streamlined the complex process of data gathering, providing an interface for real-time access to health information for users. Such a mechanism fosters autonomous health management, making health-conscious individuals active participants in their healthcare processes.
However, the growing dependency on such technologies necessitates a dialogue on their limitations and challenges. The accuracy and reliability of measurements from wearable devices are indeed imperative. Misinterpretation of erratic and inaccurate readings could lead to unwarranted panic or misguidance. Further, the overflow of health information could lead to a state of “information overload”, causing potential anxiety among users.
Additionally, with the massive data that these technologies compete to generate, data management becomes a colossal task. Ensuring end-to-end encryption of this health data and designing robust methods to protect from data breaches become priority areas to maintain patients’ trust and privacy. Solving interoperability issues to permit seamless communication between devices and platforms is another substantial challenge that requires attention.
The proliferation of healthcare wearables and IoT devices in the domain of personalized medicine marks a formidable shift in healthcare delivery – from reactive to proactive, and from generalized to individualized. The path does come with its set of obstacles that warrant careful navigation, however, the effort will indubitably lead to a transformation in health, as we know it. The promise of personalized medicine facilitated by these technologies ushers in exciting times for both healthcare enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals.
Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
Blockchain Revolutionizing Healthcare Information Management and Security
A fascinating frontier in the expedition of advancing healthcare technology is blockchain. Whilst closely associated with the world of cryptocurrency, blockchain’s decentralized, transparent, and robust security characteristics offer game-changing capabilities for tackling healthcare information management and security challenges.

Blockchain technology, with its independent and distributed nodes, creates an immutable ledger of data transactions resistant to manipulation—the audacious foundation of potential advantages in healthcare. Per the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), ensuring patient record security and privacy is a paramount issue for healthcare systems globally. With blockchain technology, enhanced security, increased transparency, and improved interoperability materialize, rendering a game changer for healthcare.
Blockchain’s potential affords unparalleled security in EHR (Electronic Health Records) management. Unlike the standard centralized database, the use of a blockchain-based system removes the risk of a single point of failure and provides an additional layer of security with each node’s validation process. The encryption techniques deployed within blockchain further shield information from cyber threats, precisely adhering to HIPAA’s stringent privacy rules.
Advancing beyond secure data storage, blockchain offers a solution to data interoperability—one of the primary hurdles of traditional digital healthcare systems. Owing to blockchain’s decentralized nature, the record once established is readily accessible without the need for complex data mapping techniques or data quality assessments. It allows for real-time data accessibility, a transformative shift from manual reconciliation and labor-intensive data extraction efforts.
Emphasizing data provenance, blockchain immensely contributes to mitigating fraudulent activities, providing an undeniable source of truth. With every transaction being permanently registered, accurate and complete record-keeping becomes uncompromised. This feature, particularly in drug supply chains, could efficiently combat counterfeit drugs, offering a tangible solution to a longstanding predicament in healthcare management.
Furthermore, enhancing patient data ownership appears feasible through blockchain technology. Therein, patients exercise increased control over who can access their data, verifying, and consenting to data requests—promoting a patient-centered approach. This functionality creates opportunities for personalized, patient-centric care and precision medicine initiatives.
Stepping into the realm of Clinical Research, blockchain liberates the potential to strengthen research integrity. The replication crisis plaguing scientific research could be addressed by adopting blockchain technology, allowing for secure storage of research data and providing an immutable, transparent record of research development.
However, as promising as blockchain technology could be, it’s not devoid of challenges. Scalability issues, substantial data storage requirements, inadequate understanding, and limited standardized protocols are potential hurdles. Recognizing these challenges and formulating adaptable solutions are crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain.
Undoubtedly, blockchain technology’s journey in healthcare information management and security is still in its infancy, and research should propel it for its effective and wider use. With growing digital data in healthcare, the influence of blockchain is expected to be more significant and transformative.
Recognizing the potential and overcoming the challenges, proponents are committed to a future where blockchain technology unlocks improved transparency and enhanced security, and more importantly, gives healthcare professionals and patients access to the right information when they need it most. Indeed, the promise of blockchain within healthcare offers an exciting frontier in the expedition of digitizing healthcare.
Conclusion
Technology has emerged as a powerful force altering the landscape of healthcare, offering a host of benefits ranging from improved efficiency, and enhanced patient care, to personalized medicine. However, the successful deployment and effective use of these technologies call for a balanced perspective, addressing their potential risks and developing solutions to overcome them.
As we navigate through the present and towards the future, the various technological advancements discussed, from Health Records Digitization, AI, ML, Telemedicine, Wearables, and IoT to Blockchain, each play an integral part in shaping a future healthcare system that’s resilient, effective, and accessible to all. The comprehensive exploration of these topics serves as a well-rounded understanding of the technological revolution in healthcare, illuminating the pathway ahead.

Hi, I’m Nathan Cross, a writer and avid reader who loves crafting articles for newspapers and online platforms. Words are my passion, whether I’m telling stories, sharing insights, or sparking conversations. When I’m not writing, you’ll find me lost in a book or out on the baseball field, enjoying the game that keeps me grounded. Writing, reading, and baseball—these are the things that define me.